Cognitive biomarkers are important because they let us know in advance of disease if we are headed in the wrong direction. Dr. Bredeson says the most frequent question he receives is “Why should I get these tests? What if my results aren’t good?”
Bredeson points out that three new biomarker results show pre-symptomatic risk, in time to begin preventive strategies. Having positive markers does not automatically mean that you will decline. Bredeson’s early trials indicate that these markers can be reversed. These markers can be monitored every six to twelve months to assess the impact of treatment strategies.
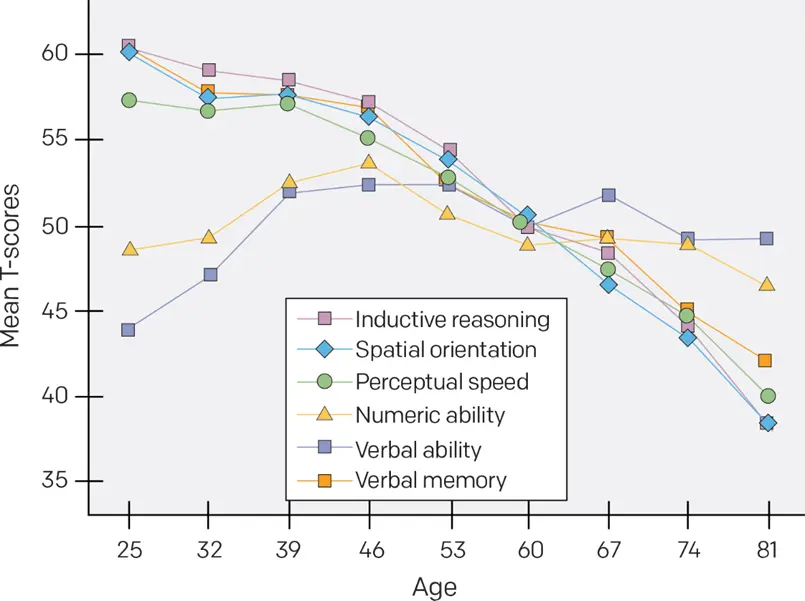
The graph below shows that cognitive decline accelerates after age 40 years. Sadly, many health professionals will tell you that there is nothing you can do about this, but this is not true. With the right strategies, cognitive improvement can be seen in six to 12 months.
The availability of these new serum biomarkers is unprecedented. In the past expensive PET Scans and lumbar punctures had to be performed to obtain this data. In fact, this triad of biomarkers is more sensitive than PET Scans and spares you the effects of radiation from the scans and invasiveness of a lumbar puncture. (NOTE the insurance copay for a PET scan is higher than the cost of the blood test.)
So, what exactly are these biomarkers?
The Biomarkers
-
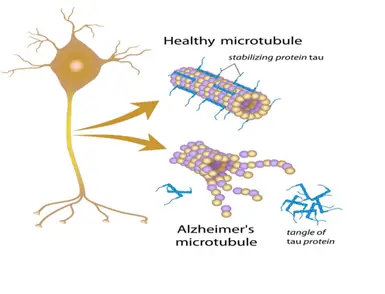
- The first, and perhaps the most important marker, is p Tau 217. This is a specific biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. It serves as an early warning sign and as a means of tracking treatment progress. The sensitivity of this test is 95%.Tau is a protein that is found in the brain. In health, it functions to maintain the microtubules within neurons through which chemical signals are sent across the cell. In disease, phosphorus can be attached to these Tau proteins. The phosphorylated proteins become sticky and form tangles. Phosphorylated Tau can no longer maintain the integrity of the nerve’s microtubules.P Tau levels increase with disease severity and decrease with effective treatment, making it an effective biomarker of disease and treatment effect. It generally takes six to twelve months to lower p Tau levels.
New data has been found in the current ReCode Trail regarding p Tau 217. This marker will be falsely low in obese people. Dr. Bredeson cited a case when a person lost 30 pounds and consequently the p Tau 217 rose.
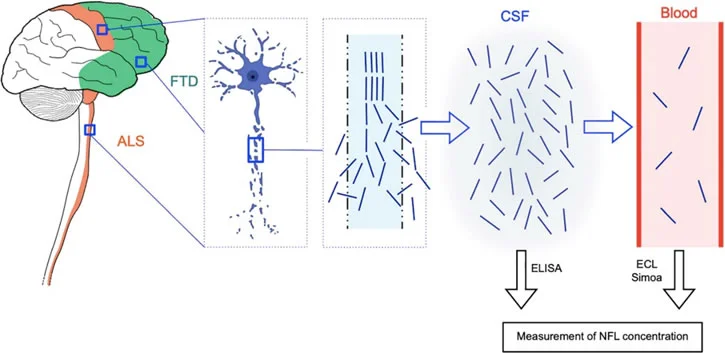
- Neurofilament light proteins (NfL) are specifically found in the axons of neurons. Neurofilaments are released from neurons due to almost any injury or disease, other than Alzheimer’s. NfL levels increase proportionately according to the degree of axonal damage. It is a non-specific marker but has been useful in identifying inflammatory, neurodegenerative, traumatic, and cerebrovascular diseases and in MS.
- Glial filament acid protein (GFAP) is found in the astro glial or immune cells of the brain. Elevations of this marker indicate brain inflammation and it is a marker for all-cause dementia. Elevations are also often seen in persons with brain fog due to Covid. Bredeson believes that Covid-related brain fog may be the first step towards Alzheimer’s disease.
These biomarkers can be detected 18 years before symptoms are evident.
Where Can I get these tests?
Although LabCorp and Quest have these tests on their menus, Dr. Bredeson states that they do not have the accuracy of the BrainScan Lab which uses specialized laboratory platforms for testing. Testing from BrainScan can be obtained with a provider order. As of May 2024, a discounted cost of $629 is available for 90 days. This cost is lower than the copay for a PET Scan.
The testing requirements are:
- Age 30 or over
- Physician request
- Family history of early onset Alzheimer’s
- Genetic screen test for Alzheimer’s
For pre-symptomatic assessment, it is recommended to test every five years until age 50. After age 50 testing is recommended every two years. Persons with intermediate or high results will be directed to enroll in the ReCode program. Persons with low results will be encouraged to monitor cognitive assessment tests.
A new tau called brain derived or BD tau, will be coming out in the future. This will identify how aggressive the disease is. A high BD tau plus a high p Tau 217 is a concerning sign. These markers will guide the need for intensity of treatment.
- The first, and perhaps the most important marker, is p Tau 217. This is a specific biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. It serves as an early warning sign and as a means of tracking treatment progress. The sensitivity of this test is 95%.Tau is a protein that is found in the brain. In health, it functions to maintain the microtubules within neurons through which chemical signals are sent across the cell. In disease, phosphorus can be attached to these Tau proteins. The phosphorylated proteins become sticky and form tangles. Phosphorylated Tau can no longer maintain the integrity of the nerve’s microtubules.P Tau levels increase with disease severity and decrease with effective treatment, making it an effective biomarker of disease and treatment effect. It generally takes six to twelve months to lower p Tau levels.